statFor some women, it's about making an elegantement at special events or being a couple…
What Is “Swayback” and How Can It Be Treated?
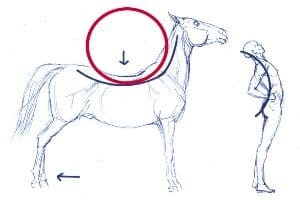
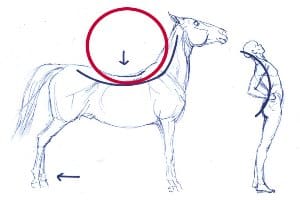 “Swayback” is the common term for excessive lordosis (aka hyperlordosis). It is a spine disorder that involves an extreme inward curvature of the lumbar area—that is, just above the hips. Swayback (also called saddle back, due to the fact that some horses can experience a similar condition) makes the backside appear much more prominent due to a forward pelvic tilt. Common among ballerinas and other dancers, this condition can also affect anyone at any age, and there are a number of potential causes.
“Swayback” is the common term for excessive lordosis (aka hyperlordosis). It is a spine disorder that involves an extreme inward curvature of the lumbar area—that is, just above the hips. Swayback (also called saddle back, due to the fact that some horses can experience a similar condition) makes the backside appear much more prominent due to a forward pelvic tilt. Common among ballerinas and other dancers, this condition can also affect anyone at any age, and there are a number of potential causes.
The excessive arching associated with swayback puts unusual stress on the lower spine, causing pain (often at the inward curve of the lower back while standing or squatting) and potentially affecting mobility. Without proper treatment, swayback may also increase the risk of herniated discs.
Potential causes of hyperlordosis (summary courtesy of WebMD):
- Achondroplasia, a disorder in which bones do not grow normally, resulting in the short stature associated with dwarfism.
- Spondylolisthesis, a condition in which a vertebra, usually in the lower back, slips forward.
- Osteoporosis, a condition in which vertebrae become fragile and can be easily broken (compression fractures).
- Obesity, or being extremely overweight.
- Kyphosis, which is a condition marked by an abnormally rounded upper back.
- Discitis, the inflammation of the discs between the bones of the spine, most often caused by infection.
- Benign (harmless) juvenile lordosis—that is, lordosis in children. This often fixes itself as the child grows.
Diagnosing swayback usually entails a chiropractor or other qualified healthcare professional reviewing a patient’s medical history and performing a physical exam. He or she may also use imaging technologies such as x-rays, bone scans, MRIs, or CT scans as part of the process. While the physical examination may vary somewhat from physician to physician, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) describes the basic approach this way:
“The health care provider will perform a physical exam. The [patient] may be asked to bend forward, to the side, and to lie flat on a table so that the spine can be examined in a variety of positions. If the lordotic curve is flexible (when the [patient] bends forward the curve reverses itself), it is generally not a concern. If the curve does not move, medical evaluation and treatment are needed.”
Additionally, if the patient is suffering from pain, tingling, numbness, muscle spasms or weakness, sensations in his or her arms or legs, or changes in bowel or bladder control, the doctor may order a neurological assessment.
As for treatment, the NIH says, “Most of the time, lordosis is not treated if the back is flexible. It is not likely to progress or cause problems.” Patients whose backs are flexible may be able to improve their condition at home by sitting less, stretching their hip flexors regularly, and stretching their upper bodies often (using a resistance band can help considerably).
If the back is not flexible, treatment is likely needed. Cedars-Sinai Medical Center describes the range of options this way:
“If the doctor decides that conservative treatment is best…[treatment] may include drugs to relieve pain and swelling, physical therapy to build strength and flexibility and to increase range of motion, braces to control the growth of the curve (especially in children and teens), and reducing excess body weight… If the curvature is severe and causing other symptoms, spinal instrumentation, artificial disc replacement and kyphoplasty are all potential surgical treatments for lordosis.”
For patients with swayback, chiropractic curve rehabilitation aims to re-establish the normal spinal curve in order to improve posture, decompress the spine and slow or stop the progress of disc degeneration. In many cases, this can be achieved without surgery or drugs using a combination of traction techniques, spinal molding blocks and lifestyle modifications.
If you notice any symptoms of swayback in yourself or in your child, it is important to seek proper medical attention. Doctors of Chiropractic are experts in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal problems and are specially trained to help patients suffering from spinal conditions. We can help! Call or visit our office today!